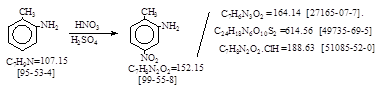| [打印本页][打印选项] |
| C.I. 冰染重氮组分12 (C.I. 37105) 生产工艺。 CAS号 [99-55-8] |
C.I. 冰染重氮组分12 (C.I. 37105) 生产工艺。 CAS号 [99-55-8]
CAS名:Benzenamine, 2-methyl-5-nitro-
LookChem网登录108家。 历史参考文献:Beil. 12, 844; E1, 392; E2, 459.
Benzenediazonium, 2-methyl-5-nitro-
[27165-07-7] = 重氮体。LookChem网登录3家。
Benzenediazonium. 2-methyl-5-nitro-, naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate. [49735-69-5] = 稳定重氮盐。LookChem网登录2家。
Benzenamine, 2-methyl-5-nitro-, hydrochloride. [51085-52-0] = 2-甲基-5-硝基苯胺盐酸盐。 LookChem网登录3家。
用途:棉织物的染色和印花。合成酸性黑28。直接蓝39。颜料红8, 17, 22, 114, 162。 反应类别:硝化。
英文原版《Colour Index》。C.I. 37105.
C.I. Azoic Diazo Component 12. 发明者:Winther, Laska, Zitscher 1911年。
生产工艺参考文献:FIAT 764 – Echtscharlachsalz G. Echtscharlach G Base neu. 无BIOS,FIAT和PB报告说明。
BIOS 986, 426.(=胶卷PB 77764)。 4-Nitro-o-toluidine
(Echtscharlach G Base) alt.
(Ludwigshafen). 英国人摘译自德文。
反应式:本人有加注,译者未说明资料来源。
Manufactured by the mixed acid nitration of o-toluidine. Yield: 96.5% theory.
The materials usage per 1,000 kgt. Of product is:-
750 kg. o-toluidine;
3,875 kg. 98% sulphuric acid; 462
kg. nitric acid 100%; 11 kg. Esbit BSH
500; 420 kg. Ammonia (for cooling).
The average monthly production in tones during the years 1938-1944
inclusive was 1.6, nil, 0.2, nil, nil.
Echtscharlach G Base New – this was manufactured similarly except that
4.5% 6-nitro-2-toluidine was incorporated.
BIOS 1149, 19-23.(=胶卷PB 80376)。 Fast Schrlet G Base =
4-Nitro-o-toluidine. (Ludwigshafen). 英国人译自德文。
This important Base is essentially 4-nitro-o-toluidine containing a
small proportion of the 6-nitro-isomer(抄注:CAS号 [603-83-8]). o-Toluidine
is nitrated in sulphuric acid and the mixture drowned out to give the
sulphates; by careful control of the isolation conditions the correct amount
(4-5%) of the more soluble 6-nitro-o-toluidine sulphate is retained. Basification then give the free base sold as
Fast Scarlet G Base. By modification of
the isolation conditions a pure 4-nitro-o-toluidine free from isomers can be
obtained. Details of the process (date:
8.8. 40) are given below:
Plant: 设备:略,不再抄录。
Materials: o-Toluidine; Sulphuric acid 98%; Nitric acid
98%; Ammonia 25%;
Esbitkohle.
Process: (a) Nitration. 操作步骤:(a) 硝化。
The two vessels (700 A and B) are each charged with 3390 kg. of 98%
sulphuric acid. With good cooling there
is run into each during 1.5 hours, 600 kg. o-toluidine so that the temperature
does not rise above 35℃. It
is cooled to -12℃. and stirring continued until all the lumps
of o-toluidine sulphate have disappeared (Total time from start, 5 hours). The two measure vessels (13 B and C) are
charged with 345-350 kg. 98% nitric acid, and a charge of 353 kg. 98% nitric
acid run from each into each nitrator with a temperature not above -10℃. The additions are timed thus:
1-318 kg. at not more than 16-17 kg. per 30 min. 318-338 kg. at not more than 12 kg. per 30
min. 338-353 kg. at not more than 4 kg.
per 30 min.
Total time of addition 14-17 hours in A or 12-13 hours in B. The batch is then stirred for 0.5 hour.
Test: (a) A nirometer test must show no NO(氧化氮). (b) A
sample is tested after 300, 348, 349 and 350 kg. nitric acid addition as
follows: 20 drops of the nitration mixture (ca. 1 g.) are treated with 3 drops
of a solution of 5 g. of sodium dichromate in 150 cc. 96% sulphuric acid and
shaken until well mixed. Then 0.5 cc.
ice-water are added. By this test free
o-toluidine gives a blue colouration (before dilution); the reaction is
considered complete when the deep blue colour becomes a grayish-blue. In the absence of o-toluidine, the addition
of the water produces a yellow colour.
(b) Isolation of sulphate. 4-硝基-2-氨基甲苯硫酸盐的分离。(抄注,其CAS号尚未找到)。
When the nitration is finished, the vessel (701) is charged with 2650
l. water (for the 1st batch of a campaign).
For subsequent batches not water is first added at 35-40℃. to dissolve the sulphate remaining round the cooling coils from a
previous batch. Sufficient water is then added to give a volume of 2750 l.
The two nitrations (from 700 A and B) are then worked up separately by
running each into (701) in about 4 hours.
The temperature is rises during the first 2.5-3 hours to 65℃., and further increase is checked by slight cooling. It is then cooled to 25℃. in about 2 hours and then dropped to the nutsche, the mother liquor
being collected in the receiver (No. 703 A).
This mother liquor has a Sp. Gr. Of 1.382-1.410 (40-420Be’).
The quality of the final derived base depends on the efficiency of
filtration. The correlation between the
weight of filter cake (from 2 batches) and the C. P. of the derived base is
shown below:
Kg. sulphate / C. Pt. 6000-6200 / 103.5-103.3。
6200-6400 / 103.3-103.1。 6400-6600 / 103.1-103.1。
6600-6800 / 103.0-102.8。
6800-7000 / 102.8-102.6。
A C. Pt of 1030 (not corrected) is aimed at. The quantity of mother liquor is 2550-2800 l.
(3600-3900 kg.) – this is discarded. To
obtain a constant content of the 2,6-isomer the filtration must be done very
carefully as follows:
The nutsche-cake must always be covered with liquor until all the
batch has been run down. Vacuum is then
applied during 25-30 min. and in this time the cake is pressed down twice. It then weights 3300 kg., and should be a
bright ivory colour – not yellow. A
yellow shows that too much nitric acid has been used.
If the nutsche-cake is bumped and pulled dryer so that it only weights
1800-1900 kg., a product of very low isomer content is obtained which does
under the name of “p-Nitrotoluidine 100% sulphate M. W. 152”.
(c) Basification. 碱化。
The vessel (711 B) is charged with 2200 l. water and 2600 l. mother
liquor from a previous batch from (703) (see below), and heated with direct
steam. The nutsche-cakes from two
nitrations (6600 kg. wt.) are charged together, and then 4000 kg. 25% ammonia
is pimped in under the surface during 2-2.5 hours. The temperature rises to 60-61℃. and prevented from rising higher by circulating water at 55℃. through the coils. It is then
cooled in 3 hours to 25℃. and dropped to nutsche (702 A), the mother
liquor being pumped to vessel (703). The
vessel is washed but with 250 l. water and then with 1000 l. water (or with
subsequent wash liquor, see below).
The mother liquor and this first wash (up to 100Be’) is collected in
(703) and when this is full into (703 A).
The combined volume is 10 m3. A
part (2600 l.) is charged into (711 B) for a subsequent batch and the remainder
into (711 A) for work up as described later below. This liquor has a Sp. Gr. Of 1.180-1.90
(22-230Be’.) and 100 cc. = 0-1 cc. N/1 NaNO2.
The nutsche-cake is then washed further with two lots of 800 l. water
until neutral to litmus, and then further with 10-15 m3 water until only 0-20Be’.
(Sp. Gr. 1.001) and free from ammonium sulphate. These wash liquors go to drain. The nutsche-cake contains 25% moisture. It is dried at 60-65℃. for 24 hours in a Schilde dryer on rubber covered from trays.
2 Nitrations require 3 dryings.
6 Wagons of 48 trays each. The
dried material (test for completeness) is ground in a “Schlagscheibe”
(d) Recovery of ammonium sulphate.
硫酸铵的回收。
The residual mother liqur in 703 and 703 A is blown to 711 A where two
batches are collected. It is made
slightly alkaline to Brilliant Yellow with ammonia (100-200 kg.) and, after
addition of 10 kg. Esbitkohle, is filtered through press (712) under gravity to
receiver (109). It is then pumped to a
storage wagon and sent to Oppau. It
should be slightly greenish-yellow in colour, Sp. Gr. Not below 1.19. 1 Batch (2 nitrations) gives 10.8 m3 ammonia
sulphate solution (Sp. Gr. 1.195-1.20 or 34-35%). The screening press is only cleaned after 10
batches and the contents are discarded.
Yield: Per batch of 2 nitrations = 1440 kg. Fast Scarlet G Base
new. Theoretical yield = 142% by wt. on
o-toluidine.
Press yield = 120% by wt. on o-toluidine = 84.5% of theory. The recovery of ammonia as ammonium sulphate
is approx. 95%.
Quality: 4-硝基-2-氨基甲苯 质量。 Tested colorimetrically and by I. G. No. 415.
1. Diao value to be
98-99%. 2. Diazo solution to be as clear as that of the
type sample. 3. C. Pt. 102-104℃.
At 103-1℃. the 6-nitro-o-toluidine content is 4.4%.
细田豊 《理论制造染料化学》1957年。 P. 509. 4-ニトロ-2-トルイジン (ファストスカ- レット G ベ- ス) 译自PB 80376.
(a) 硝化:3 m 3铸铁釜に98% 硫酸3390 kgを入れ,350以下1.5 hでo-トルイジン600 kgを加え,冷却しながらよく搅拌して溶し,98% 硝酸350 kgを-100以下で终りに近い程だんだんおそく约15 hで加え,0.5 h搅拌する。
(b) 分离:硝化物を水2.7 m3に650をこえぬように数时间かかつて排出し,250まで冷し硫酸盐をヌッツェで滤過する。异性体の含量を一定にするために滤過のを程度ケ- クが3.3 t 位になるように调节する。
(c) 中和:水1.1 m3および前回母液1.3 m3に硫酸盐ケ- キを加え,25%アンモニア2 tを液面下に600以下で加え,250に冷して滤過し,水130 l で洗い滤洗液は硫安回收に向け,ケ- クを滤液が0-20Be’ になるまで水洗し,60-650で亁燥する。 1220 kg, 收率84.5%,cp 102-1040 (103.10で6-ニトロ-o-トルイジン含量4.4%)。 ジアゾ价98-99%。
张澍声 《精细化工中间体及产品生产工艺》2006年。 P. 385. 2-氨基-4-硝基甲苯。 译自BIOS 1149, 19-23.
2-氨基-4-硝基甲苯含有少量6-硝基异构体是一种重要的色基,G色基。邻甲苯胺在硫酸中硝化,混合物压出,得到硫酸盐。仔细控制分离条件,更易溶解的6-硝基-2-氨基甲苯硫酸盐(4-5%)留下。将分离出的4-硝基-2-氨基甲苯碱化,得到游离胺。如果改进分离条件,可以得到2-氨基-4-硝基甲苯。
(1)硝化:在两个3000 L铸铁硝化锅(浆式搅拌器,转速65 rpm,冷却蛇管用氮气冷却)中,各加入3390 kg 98% 硫酸,在很好冷却下于1.5小时内各流入600 kg 2-氨基甲苯,要使温度不超过35℃。冷却到 -12℃,继续搅拌,直至所有的块状2-氨基甲苯硫酸盐完全消失(从开始总的时间为5小时)。向两个500 L硝酸计量槽中加入345-350 kg 98% 硝酸,并向每个硝化锅中加入353 kg 98% 硝酸,温度不超过 -10℃。加入速度是这样控制的: 1-318 kg 每半小时不超过16-17 kg。
318-338 kg 每半小时不超过12 kg。
338-353 kg 每半小时不超过4 kg。总的加入时间A锅14-17小时,B锅12-13小时,反应物再搅拌0.5小时。
检验A – 测氮管检验必须无NO。 检验B – 在加入300,346,348, 349和350 kg 硝酸后,取样检验如下:取20滴硝化混合物(约1 g),用3滴重铬酸钠在150 ml 96% 硫酸中的溶液处理,震荡至很好混合,然后加入0.5 ml 冰 – 水。经这一试验,游离2-氨基甲苯得到蓝的颜色(稀释前);当深蓝色变成灰蓝色,说明反应已经完成。 没有2-氨基甲苯时,加水产生黄色。
(2)硫酸盐的分离:硝化完成后,在19.5 m3衬砖锅(30 rpm浆式搅拌器,铅冷却蛇管)中,加入2650 L水(第一锅),在以后的批次中先加入35-40℃的热水,以溶解留在冷却蛇管周围的硫酸盐(上批反应的),然后加水至总体积为2750 L。
两个硝化锅A和B分别进行处理,于约4小时内各流入19.5 m3锅中,在最初2.5-3小时上升到65℃,进一步上升则以微冷却纠正。然后于2小时内冷却到25℃,进行抽滤,母液收集在接受器中,其比重为1.382-1.410。 最后得到的胺的质量取决于过滤效率,滤饼重量(两批)和胺的结晶温度之间的关系如下:
硫酸盐(kg)/ 结晶温度℃。 6000 -6200 / 103.5-103.3; 6200-6400 / 103.3- 103.1;
6400-6600 / 103.1-103.0; 6600-6800 / 103.0-102.8;
6800-7000 / 102.8-102.6。 结晶温度(未校正)103℃是要求值,母液数量为2550-2800 L(3600-3900 kg),弃去。
为了得到固定含量的2,6-异构体,过滤必须非常小心进行如下:滤饼必须总有液体覆盖,直至所有反应物流下。然后于25-30分钟内抽真空,在这一时间内滤饼压紧两次,其重量为3300 kg,应是嫩乳白色,不是黄色。黄色表明已经使用太多硝酸。如果滤饼是开裂了,并已抽干,则重量仅有1800-1900 kg,产品的异构体含量太低,应称为100% 2-氨基-4-硝基甲苯硫酸盐。
(3)碱化:在15600 L铸铁锅(25 rpm橡胶包复浆式搅拌器)中,加入2200 L水和2600 L上批母液,用直接蒸汽加热。两批硝化的滤饼6600 kg 一起加入,然后于2-2.5小时内从表面下部压入4000 kg 25% 氨水。温度上升到60-61℃,为了防止高于此温度,经过蛇管循环55℃的水。然后于3小时内冷却到25℃,抽滤,用250 L水洗涤,再用1000L水洗涤(或者用随后的洗涤液,见下面)。
母液和第一次洗水(比重1.074)合并,总体积为10 m3。2600 L加入到另一15600 L铸铁锅中,用于下一批碱化。其余仍回到15600 L锅中,其比重1.180-1.190,每100 ml相当于0-1 ml N/1 NaNO2。
滤饼用800 L水洗涤两次,至石蕊试纸呈中性,然后再用10-15 m3 水洗涤至比重为1.001,并不含硫酸铵。这些洗水都弃去。滤饼含25% 水分,放在橡胶包复的盘中,在60-65℃干燥24小时。两锅硝化料需分3批干燥。每次6车48盘。然后研磨。
(4)硫酸铵的回收:将两批的母液收集在15600 L铸铁搅拌锅中,用100-200 kg 氨碱化至对亮黄试纸为微碱性,加入10 kg活性炭,在木压滤机中压滤。滤液用槽车送往另一地方处理。颜色为微绿黄色,比重不低于1.19。每批(两锅硝化物)得到10.8 m3 硫酸铵溶液(比重1.195-1.20,或34-35%)。每批两硝化锅得到1440 kg 2-氨基-4-硝基甲苯,收率84.5%。以硫酸铵回收的氨约95%。
质量指标:1. 重氮值98-99%; 2. 重氮溶液的清晰度与标准样品相似; 3. 结晶温度102-104℃;在103.1℃时6-硝基-2-氨基甲苯含量为4.4%。
德文原件:
PB 17658. Reports of the
Intermdiate products. 1309页。 1935-1936年。
PB 17658, 1933-1935. Prevention
of clumping of the “Echtscharlach G Base” . 研究报告,未抄录。
PB 25602. Manufacturing methods of the “Basefabrik” and other
manufacturing methods. 1430页。美国1946年公布。
PB 25602, 137-140. No. 3718. “Echtscharlach
G Base” . 德文生产工艺。未抄录。
PB 25625. Manufacturing methods
of preparation of dyestuffs, as disclosed through T. E. A. Büro documents. 1171页。1932-1939.
PB 25625, 490-496. Directions
for producing “Echtscharlach G Base neu”.
德文生产工艺,本人抄录如下。
Fabrikationsvorschrift für Nr.
3718 Echtscharlach G Base neu. Mol. 152
= 4-Nitro-2-toluidin. Ludwigshafen. 1937年3月28日。
Apparatur: 设备:略。
Ausgangsmaterialien: 原料: o-Toluidin; Schwefelsäure
98%; Salpetersäure; Ammoniak 35%;
Esbitphle.
Arbeitsweise: 抄注步骤:
In die Kessel (700 A u. B) werden je 3,310 kg 98% eingewegen (Abstich
105.5 cm). Unter Tiefkühlung fliessen
aus Messgefäss (42) in 1.5 Stunden je 586 kg o-Toluidin bis zu 350 (In 42:85
cm, Abstich in 700 A 136.5, in 700 B 136 cm bei 350). Es wird auf -120 gekühlt und gerührt bis
keine Brocken von Toluidinsulfat mehr vorhanden sind. (Dauer von Beginn an ca.
5 Std.). In die Messgefässe (13 C u. B)
werden je 345-350 kg Salpetersäure 98% gepumpt.
Davon fliessen prokessel 345 kg Salpetersäure 98% nicht über -100 so zu,
dann von 1-310 kg nicht mehr als 16-17 kg pro 30 Minuten von 31-330 kg nicht
mehr als 12 kg Pro 30 Minuten, von 330-345 kg nicht mehr als 4 kg Pro 30
Minuten einlaufen. Einlaufzeit in A
14-17, in B 12-13 Std. Es wird 0.5
Stunde nachgerührt. Die Nitrometer Probe
darf kein NO mehr ergeben. Proben bei
300 kg, 343, 344 und 345 kg Salpetersäure.
Sie sollen moglichst hell, d. h. Etwas hellgelb sein. Die Probe mit 300 kg ist immer etwas dunkler.
(Abstich in 700 A/B 143.5 cm bei -120).
In Kessel (701) werden bei der ewrsten Aufarbeitung 2650 Ltr. Wasser
(=54 cm) vorgelegt. Bei den folgenden
Aufarbeitungen wird das an Wänden und Kühlschlangen angeschlagene Sulfat erst
mit 35-400 warmem Wasser abgespritzt und soviel Wseer vorgelegt, dass die Lösung
der Rückstande 3000 Ltr. =61 cm bei 350 misst.
Die Kessel (700 A u. B) werden nacheinander und getrennt aufgearbeitet
wie folgt: In ca. 4 Stunden läuft der Kesselinhalt nach (701). Die Temperatur steigt dabeo auf 650 Höchersteigen
wird durch ganz schwaches Kühlen verhindert.
In etwa 2 Stunden wird auf 250 gekühlt und das Sulfat auf Nutsche (702
B) mit Druckfass 703 abgesaugt. Die Mutterlauge
misst 42-430Be‘. Sie wird in (711 A)
weiterverarbeitet. Es fall 2550-2800
Liter oder 3600-3900 kg an. Sie wird auf
Ammonsulfat (s. unten) weiterarbeitet.
Um ein Sulfat mit konstanten Gehalt an dem in der Mutterlauge befindlich
2,6-Isomeren zu erhalten, muss das Absaugen stets in gleicher Weise wie folgt
vorgenommen werden; Man lässt auf der Nutsche zunnächst frei ablaufen, bis
alles auf der Nutsche ist. Dann wird
25-30 Minuten Vacuum angehängt und in diessen Zeit 2 mal durchgestumpft. Das Nutschegut wiegt dann etwa 3000 kg. Es soll hellelfenbeinfarben, nicht gelb
sei. Gelbfärbung rührt von zuviel
angewandter Salpetresäure her.
Nutsche man so stark ab, dass des Nutschgut nur ca. 2400 kg wiegt, so
erhält man ein Produkt mit geringeren Isomerengehalt, das unter der Beseichnung
„p-Nitro-tolidin 100% Sulfat MG 152“ als solche abgegeben wird.
In (711 B) werden 4100 Ltr. Wasser = 90 cm vorgelegt und mit direkten
Dampf auf 350 geheizt. Gleichzeitig wird
das Nutschegut von 2 Nirierungen d. i. ca. 6000 kg = 1 Partie eingetragen.
Abstich 185-195 cm bei 350. Dann werden
ca, 4000 kg Ammoniak 25% innerhalb 2-2.5 Stunden unter unpumpen unter die
Obergläche eingeleitet. Die Temperatur
steigt dabei auf 60-610 und wird durch Anstellen des in die Umpumpleitung
eingeschalten Kühlere bei etwa 550 an Höhersteigen verhindert. Abstich ca. 260 cm. In etwas 3 Stunden wird auf 250 gekühlt und
auf Nutsche (702 A) mit Druckfass (703) abgesaugt. Der Kessel (711 B) erst mit 250 Ltr. Wasser
und dan noch mit 1000 Ltr. unter Umpumpen nachgespült. Die Spülwasser werden als erstes Deckwasser für
(702 A) verwandet. Die zu 100Be‘ geht
die Waschlauge nach (703), von da an noch (703 A). Die Mutterlauge und erst Waschlauge ergibt
ca. 10 m3. Sie wird in (711 A)
weiterverarbeitet. Man stumpft 2 mal
durch und wäscht noch mit ca. 800 Ltr. Wasser bis lackmusneutral und weiteren
ca. 10-15 m3 Wasser bis die Waschlauge zur noch 0.20Be‘ misst und fest keinen
Ammonsulfatgehalt mehr anzeigt. Dei
Waschlauge von (703 A) geht in den Kanal.
Das Nutschgut enthält noch ca. 25% Wasser. Es wird im Schlidetrockner uaf gummierten
Eisenblechen bei 60-650 in ca. 24 Stunden getrocknet. 2 Nitrierungen beanspruchen 3 Schränke d. i.
6 Wagen a‘ 48 Bleche. (Probe auf Trockengehalt).
后面部分过去未抄录。(抄注: 这里要说明的是为什么英国人和美国人的译文没有资料来源!)
PB 70422. Reports on organic dyes 等。 837页。 1933-1946年。
PB 70422, 2128-219. Fast
scarlet Salt G. By Keller 1933年2月21日。 未抄录。
PB 70423. A Collection of
Reports on dyes. 937页。
1934-1945年。
PB 70423, 3063-3082. Echtscharlach
G Base. 德文生产工艺。 未抄录。
PB 73616. Reports on and
Instructions for production of chemical intermediates. 162页, 1940-1946年。
PB 73616, 1459-1464. Echtscharlach
G Base. 德文生产工艺。未抄录。
PB 74027. 本人未抄录美国人提供的胶卷目录。
细田豊 《理论制造染料化学》 1957年。 ファスト スカ- レト ソルト G。 译自PB 74027.
反应式:本人有加注。
エナメル引釜でファストスカ- レットGベ- ス100 kgを600の水413 lとまぜ,盐酸387 kgを徐加しブラインで -5 - -10に冷し,NaNO2 465 kg(102.5%)の50% 液を150以下で0.5 h に加え20 m搅拌後,滤過し水133 l で洗う。1.1 m3。これをア- ムストロンゲ酸208.5 kg (110%) + 水400 lに落し1 h 搅拌,100に冷し(1.7 m3)滤過,250 气压で压榨する。ケ- ク350 kg。
PB 74386. Production of dyes
and intermediates. (BIOS Microfilm Reel
FD 2736/46). 100页。
PB 74386, 29-30. Sodium diazotate
of m-Nitro-o-toluidine 1941年生产工艺。未抄录。
国内历年染料专业出版物:
沈阳化工研究院染料情报组 《染料品种生产》 1978年。 P. 492-493. 大红色基 G。
只有生产工艺流程,无生产工艺文献。 生产(试制)单位:5家。
中国化工信息中心 《染料品种指南》 1995年。 P. 176. C.I. 冰染重氮组分12 (C.I. 37015)。
【主要文献】译自原版“Colour Index”. 国内生产厂。13家。
《世界染料品种 – 2000年》编写组 《世界染料品种 – 2000年》2000年。 P. 470. C.I. 冰染重氮组分 12.
参考文献:译自原版“Colour Index”.
肖 刚 杨新玮 等 主编 《世界染料品种 – 2005年》2005年。 P. 227. C.I. 冰染重氮组分 12.
参考文献:译自原版“Colour Index”.
何岩彬 主编 《染料品种大全》沈阳出版社 出版。 2018年。 P. 394. C.I. 冰染重氮组分12.
参考文献:新增:PB 25625, 490-6; PB 70422, 2128-9; PB 74386,
29-30. 说明:这是2016年本人补充的内容。
老有所为,老有所乐:
今天抄录上述历史资料,是要说明本人“老有所乐”的地方。有人说“考古”!我们的“考古”工作者,发现我们历史上就是没有文字记载。我为什么要抄录这些历史资料,是因为人家德国人的记载,从发明专利到研究开发,再到历年的生产工艺变化都有记载。当然,今天能看到它,这是以前的历史原因。
再说英国人的BIOS和美国人的FIAT,这是经他们加工过的,进口的书本。当然他们可以不告诉你资料来源。我们过去大多数单位都有。问题是国内无人整理,无人归纳,与此相对比,我为什么要去抄录日本人的书本,细田豊《理论制造染料化学》一书,他们在1957年就有BIOS和FIAT的译文,特别是德文原件PB报告。明显的是,他们不完全依靠原版《Colour Index》。这就是本人要再写上《国内历年染料专业出版物》的原因。也就是我们也要去做点《基础性的》整理工作。这里不仅仅是国外的文献资料,国内的也要有人去做。张澍声老先生的译文,是我本人抄录的重点,应该谢谢他。
陈忠源 2019年3月16日星期六。
文章作者:陈忠源 |