CAS号 [602-38-0]和[605-71-0] 生产工艺 1,8-和1,5-二硝基萘
CAS名: Naphthalene, 1,8-dinitro-历史参考文献: Beil. 5, 559.
Naphthalene, 1,5-dinitro- Beil. 5, 558; E1, 264; E2, 454; E3, 1606; E4,
1680.
用途: 有机合成。硫化染料。还原体,溶剂橙,溶剂红,溶剂蓝和有机颜料等。
生产工艺参考文献: 萘硝化产生1,5-体和1,8-体二种,按本人手头资料整理如下。
BIOS 986, 416-417.(=胶卷PB 77764). No. 231 1,5 / 1,8-Dinitronaphthalene. (I.G.
Ludwigshafen) 英国人摘译自德文。抄录如下。
反应式: 本人有加注,译者未说明资料来源。德文1,5-体为Alpha Säure ,1,8-体为Deltasäure。德文原件暂未找到!
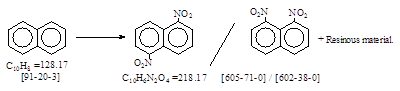
Manufactured by charging naphthalene to mixed acid,
the temperature rise being restricted to 44℃, initially. Nitration
is completed by heating to 80℃
and the batch isolated by pouring into water, cooling to 30℃, filtering and drying at 70-80℃.
The product is a mixture. Yield:
99.9%. The materials usage per 1,000
kg. of product is:
588 kg.
naphthalene. 1,840 kg. 98% sulphuric acid 100%. 730 kg.
nitric acid 100%. 7 kg. recovered
sulphuric acid 380Be’
The average monthly production in tones in the years 1938-1944
inclusive was 12.2, 3.2, nil, 11.4, 12.9, 31.2, 17.8.(历年产量)。
BIOS 1152, 43-48. (=胶卷PB 81027). 1,5- and 1,8-Dinitronaphthalene.
(Ludwigshafen). 英国人译自德文。抄录如下。
A) Crude Dinitronaphthalene: (No useful outlet had been found for all the
1,5-dinitronaphthalene, which has accumulated at Ludwigshafen to the extent of
100 tons). 粗制二硝基萘:
Plant: 设备: 以下抄录不再分项。德文原件暂未找到!(因为其中的PB报告本人未看!)
No. 200. – 1
Nitration vessel, cast iron with jacket. Plate stirrer, 25 r.p.m. Motor, 3.8 Kw., 3.4 m3 capacity。 No. 201 and No. 202. –
2 Nitration vessels, wrought iron, jacket, propeller
stirrer, 26 r.p.m., Moter, 3.8 Kw., capacity, 3.4 m3。 No. 53. – 1 Container for HNO3 of
V2A. 1.2 m3 capacity。 No. 27.
– 1 Container for HNO3 of V2A. 1.0 m3 capacity。 13 and 13 a. – 2 Container for
weighing the 98% HNO3
Approximately 1 m3 capacity。 No. 207. – 1 Stirring vessel, lead
lined and “Kerasolithiert”. Plate stirrer, 30 r.p.m. Motor, 3.7 Kw.,
Capacity 14.9 m3。 No.
204. – Nutsche, cast iron, “kerasolithiert”, 8 m2, capacity 6 m3。 No. 203 A. – Pressure egg, “Kerasolithiert”,
4 m3 capacity.
Materials: 原料: Pure
Naphthalene. H2SO4 – 98%. HNO3 –
53%. HNO3 – 98%.
Process: 操作步骤: 这一译文比较全面,英国人当时能共享,一般读者看不到,我想抄一遍也值得了!
Vesses 200
and 202, are charged with approximately 1,850 kg. of H2SO4 98%. Then 1,220 kg. HNO3 53% and 50 kg. 98% HNO3
are
Run in from container 53, the temperature rising to
about 30℃. The addition occupies 2-4 hours and the dip
of the vessel is 109-110
cm. A worm feed
transporter brings the naphthalene to the pan; a total of 590 kg. of which is shoveled
into the pan as follows:-
118 kg. in 4
hours at 340-36℃。 118 kg. in 4 hours at 360-37℃。 118 kg. in 4
hours at 360-37℃。 118 kg. in 4 hours at 370-38℃。
The addition
of the final 118 kg. of naphthalene is spread over 5 hours so that at the end
the temperature is 44℃. After this, the
Temperature is raised during 4 hours to 80℃. and kept there for 1 hour. (Test: Before
heating, nitrometer test of 2 cc. shows 18-20 cc. of
NO. After
heating, the test is 14-15 cc. of NO.).
The vessel
(207) is charged with 7 m3 of water and the nitration mixture blown in. The temperature rises of its own accord to
40-
50℃. It is cooled to 30℃. and filtered off on nutsche (204). The mother liquor is about 260Be’ (Sp.Gr.
1.220). The egg is blown to
the drain. The
product is washed, from the nitration kettle, first with 6 m3 cold water and
then with 12-14 m3 warm water. At the
end
of the washing the Be’ is down to 0.20 (Sp.Gr. 1.001)
and 100 cc. = 3 cc. N/I NaOH to neutralize.
It is then sucked dry and dried in an
oven (Schildeschrank) on aluminium trays at 70-80℃.
Yield for
Batch: 批收得率:
2Nitrators provide 2000 kg. of dinitronaphthalene
crude material. Yield of theory = 80%.
i.e. 170% of starting material.
B) Separation
of 1,5- and 1,8-dinitronaphthalenes. (Alpha Säure and Delta Säure) (1,5- 和1,8-体的分离。)
Crude
dinitronaphthalene is a mixture of about 20% 1,5- and 53%
1,8-dinitronaphthalene; the remaining 27% is composed of
resinous material.
In general, advantage is taken of the greater solubility of the
1,8-dinitro compound at elevated temperature in
ethylene dichloride.
The mixture heated to 80℃.
in this solvent is cooled to 50℃.
when the 1,5- crystallizes out. It is
filtered off and,
on cooling the mother liquor to room temperature, the
1,8-dinitro derivative is deposited. The
valueless resinous impurity remains
behind in the ethylene dichloride mother liquors.
Dinitronaphthalene (crude). 1,8-dinitro + 1,5-dinitro + Resin
1000 (100%) kg. / 100
536 kg. (100%) / 53.6 + 237 kg. (100%) / 23.7+240 kg. / 24.
Cycle of Operation and Daily Rota: 操作周期于日产量: (Rota 原文如此。)
From charging of crude dinitronaphthalen to taking the
1,8-dinitronaphthalene from the nutsches, 72 hours.
Daily production: 11/2 batches = 795 kg. “Delta Säure”
100%. (抄注:即1,8-体日产量。)
Plant: 设备: 以下抄录不再分项。
1 Dissolving wrought iron vessel, stirred tank, stock
agitator. Capacity, 12 m3. Steam jacket
heating with condenser pipe attachment。 3 Enclosed air pressure filters with cotton
or flannel。 1 -1,5-
pressure filter and 2- 1,8- pressure filters。 3 Enclosed
stirring vessels, plate stirrers, of about 5 m3
capacity. Steam jacket heating;
condenser pipe attachment (2 concentrating tanks and one storage vessel)。 4 Venuleths
(i.e. rotary type of distillation vessel), 1200 l. capacity, fitted for solvent
recovery)。 1 Large iron
separator of 250 l. capacity。 2 Suction filters (1,5- and 1,8- nutsches)
lined with porous filter tiles, enclosed.
To work at two atmospheres pressure.
Capacity about 2 cubic metres。 3 Enclosed vessels, lead-lined, one stirred,
condenser pipe attachment。 1 Iron stirring vessel; capacity 3,600 l.;
stock agitator。
Process: 1,5- 和 1,8-二硝基萘的分离操作步骤: (本资料,未见国内的研究报告有引用!)
The charging is carried out in an enclosed iron kettle
with 4180 l. (900 l. can be crude) ethylene dichloride. To this is added 1000 kg. of crude
dinitronaphthalene mixture and about 6 kg. of soda. The whole is heated to 75-81℃. and at this temperature during 11/2 hours
– 2 hours is distilled free of water.
This distillation removes a about 200-300 l. It is then changed to reflux and kept for a
further 1hour at 84℃. If solution is not complete by this time, a
further 1/2 hour’s heating given. It is
then cooled by means of the jacket to 60℃. and the jacket then emptied. From this point the cooling is allowed to
continue of its own accord until the temperature reaches 50℃. The
contents are then filtered off at this temperature through the enclosed
attached 1,5 pressure filter. This is filtrate
A. The nutsche is then washed with 6
washes of 300 l. each of pure ethylene dichloride and then sucked down to the Venuleth
with 300 l. ethylene dichloride. The
nutsche is swilled out with a further 100 l. of ethylene dichloride. 100-200 l. of water, together with 4 kg. of
soda ash, (this on account of explosion risks) are now run into the venuleth
and the ethylene dichloride is distilled off through a receiver and separator. The 1,5-dinitro is filtered off, washed twice
with water, pilled dry, and the nutsche cakes casked up. The six washes that have been used during the
processing are treated as follows. The
first three washes are returned to the storage vessel and then distilled off in
both concentrating tanks. The remaining
three washes are sent back for use in the solution vessel.
Yield: About 230
kg. of 1,5-dinitronaphthalene, M. P. 2140- 216℃. (as about 70% paste). (这一步分离得到1,5-体)。
1,8-Dinitronaphthalene: 1,8-二硝基萘: (是以二氯乙烷为溶剂进行分离!)。
The Filtrate A previously described, contains the 1.8-dinitronaphthalene.
It is returned to the concentrating tank and dry distilled until the volume
remaining is not less than 1700 l. (= 87-88 cm. dip). It is then cooled to 20-25℃. and stirred at this temperature for 2
hours. The contents of the kettle are
then filtered off on the 1,8 pressure nutsche.
The filtrate goes to a venuleth. The
nutsche is again washed with 6 washes of 300 l. of pure ethylene
dichloride. The filtrate from the first
wash goes to the previously mentioned venuleths for recovery. The five remaining washes, i.e. (2-6) are
returned to the storage vessel for distillation in both concentrating tanks to
recover the ethylene dichloride. The
residue from the venuleth contains a molten resinous deposit which is
worthless.
The residue on the pressure filter is washed down to
the two venuleths with 600 l. of pure ethylene dichloride and diluted with
100-200 l. H2O to minimize explosion risks.
The venuleths contain knife scrapers.
The ethylene dichloride is distilled off with steam and the aqueous
pasty mass left is filtered and washed once or twice. The paste nutsche-cake goes forward for the reduction.
Yield: About 525
kg. 1,8-dinitronaphthalene as about 70 paste.
(这一步分离得到1,8-体)。
Important Points:
操作要点: 以下抄录不再分项。
(1) The dry
residue left after the removal of the ethylene dichloride should not exceed 1.5%,
providing the filtration temperature has not been exceeded。 (2) The filtration on the “1,5 pressure nutsche” must
be carried out exactly with in 1℃. of the stipulated temperature, both entering and
leaving the nutsche。 (3)
The distilling off of the ethylene dichloride from the kettle and venuleth must
be carried out caustiously, as the light mixture easily foams over。 (4) The
addition of the soda ash to the 1,5-dinitro compound in the venuleth must be
sufficient to show a weak alkaline reaction。
Staring Product Impurities Test: 原料杂质测试:
The crude dinitronaphthalene should be light coloured
and give a clear solution in the ethylene dichloride. The free acid content of every batch is
estimated and should not be more then 1% free sulphuric acid.
Recovery of Solvent:
二氯乙烷溶剂的回收:
The ethylene dichloride is recovered by steam
distillation. The loss per batch is about 200 kg.
Final Product Impurities Test: 成品杂质的测试:
The moist press cake is used as such for the
manufacture of “Deltamin”. The material,
as produced with good operation, contains some 1,5-dinitronaphthalene (up to
10%). It is tested by m.p. which should be between 1450 and 155℃.
By Product:
1,5-dinitronaphthalene = “Alpha Acid”. It is technically pure and can be
stored as required.
抄注: Nutsche = 抽滤槽。 Venuleth = 真空耙式干燥器。本资料,发现细田豊未引用!
细田豊 《理论制造染料化学》 1957年。 P.
523. 1,5- / 1,8-二硝基萘。 译自PB 77764和 PB 25602.抄录如下。
(1)粗ジニトロナフタリン:
98% 硫酸1840 kg + 98% 硝酸730 kgに440からナフタリン588 kgを加え800に加热して反应を完结させ,水に排出,滤過,70-80で亁燥する。 1
t。收率99.9%。
(2)分离: (抄注:引用PB 25602.它用丙酮为溶剂进行分离。)アセトン4.2
m3に粗ジニトロナフタリン1 tを入れ,逆流コンデンサ- を開いて560に热し空气を排除した後コンデンサ -を闭じ,600に8 h加热すれば1,8-ジニトロが溶け,1,5-が滤過しやすい结晶となる。430で压滤過し,アセトン200 l
で釜すすぎ500 l x 4 で洗う。结局1,5-ジニトロナフタリン230-240 kg (mp 2110-2130),1,8-ジニトロナフタリン530 kg (mp 147-1580)を得る。アセトン损失130-140 kg。
抄注:说明作者未引用BIOS
1152, 也未找到其德文原件!所以未见二氯乙烷为溶剂的分离法。
PB 25602, 438-447.
No. 4600. 1,5-Dinitronaphthalene and 1,8-Dinitronaphthalene. 德文丙酮法分离生产工艺。未抄录。
PB 25602, 593-599.
No. 4569-0. Crude
dinitronaphthalene. 1934-1939年德文生产工艺。部分抄录如下。
Dinitronaphtalin roh und S 1934年6月21日。 (产品生产的历史经验值得参考!)
Apparatur: 设备: 以下抄录不再分项。
1 Schmiedeeiserne ausgemauertes Rührreservoir, 7.5 m3
Inhalt zum Einstellen der 60.50 Be‘ Schwefelsäure。 1 gusseisernes Messgefäss, 600 l Inhalt。 1 liegender Aluminiumdruckfass, Inhhalt 20 cbm für
conz. Salpetersäure。 1
Aluminium-Messgefäss für Salpetersäure 500 l Inhalt。 3 Schmiedeeiserne Nitrierkessel mit Heiz- u. Kühlbad,
Inhalt 1100 l。 2 Verbleite Holz-Rührbütten je 7 m3。
1 betonierte ausgemauerte Nutsche, 11.5 qm. Fläche。 1 gusseisernes
ausgemauertes Druckfass, 1800 l Inhalt. Zum Trockensaugen. Ferner für
Dinitronaphtalin S。 1
Schmiedeeiserne Kugelmühle。 1
Schmiedeeiserne Rührdruckfass, Inhalt 2000 l。
1
Waschfilterpresse 1.20 x 1.20, Baumwollfiltertücher。
Verfahren: 操作步骤: 德文原件按投料量分项,以下抄录也不再分项!
In einem Sulfierkessel werden 1130 kg Schwefelsäure
60.50Be‘ (Bem. 1.) und 83 kg in stücke zerschlagesem tech. Ammonnitrat (aus
Oppen. Gehalt am NH4NO3 ca.98%) ca. 1 Stunde miteinander verrührt, bis das
Ammonnitrat gelöst ist. Nach Zugabe von 240
kg Salpetersäure 98% werden mittels Schnecke bei 35-360 276 kg Naphtalin gewerden
eingetragen (Bem. 2.) und zwar je 20 kg in 1 Stunde. Nach dem Eintragen wird
innerhalb 3 Std. auf 800 aufgeheizt und 2 Std. bei dieser Temperatur gehalten (Probe
). Dann wird auf 250 abgekühlt und er
Inhalt von 3 Kesseln in eine der Rührbütten in 3800 l Wasser abgelassen. Es wird sofort auf einer der Nutschen
abgesaugt und das Nutschgut mit Wasser säurefrei gedeckt. Mutterlauge und Deckwasser laufen durch den körting
ommittelbar in den Kendal, das Druckfass word erst am Schlusse angehungt, an
die Ware eingermeseen trocken zu saugen.
Die Fertigtrocknung erfolgt im Lufttrockeschrank bei einer hochst Temperatur
von 700. Für Dinitronaphtalin S wird die
– Nitrierkesseln = 2200 kg Naphtalin entsprechende Menge auf 3 mal in einer
Kugelmühler zusammen mit je 300 l Wasser und 20-25 kg Soda innerhalb 6-8 Std,
fein vermuhlen, mittels Druckfass gewaschen und in Lufttrockenschrank nicht über
800 getrocknet.
Ausbeute: 100
kg Naphtalin. 170 kg Dinitronaphtalin in
roh oder S. M.G. 210 = 98% der Theorie.
Bemerkungen: 注意事项:
Bem. 1. Die 60.50Be‘ Schwefelsäure wird hergestellt
durch Mischen von 362 Gewichtsteilen abfalllschwefelsäure 380 und 638
Gewichtsteillen Schwefelsäure 670.
Bem. 2. Die Mischung von Schwefelsäure 60.50 und
Salpetersäure 98% in den angegebenen Verhältins ergibt winw Nitriersäure von
58.5-590Be‘ mit 62.5% H2SO4 und 20.5% HNO3 in welcher Dinitronaphtalin gerude
schwebt. Wird unterhalb 350 Naphtalin
eingetragen, so reagiert das Naphtalin zu träge. Tritt dann durch Erwärmung wieder Reaktion
ein, dann ballen sich die Teilchen zusammen und bringen unter Umständem durch
Klumpesbildung den Rühren zum stabenbleiben.
Ahnliche krocheinungen troten bei am raschen Eintragen des Naphtalin
ein.
Probe: 取样分析:
2 g der von Dinitronaphtalin abgetrennten Mischsäure
werden in Nitrometer mit ca. 10 cm3 Schwefelsäure verdunnt. Bei beendigter Nitrierung werden in der Regel
ca. 8 cm3 NO entwickelt.
Genauer ist die Beendigung der Nitrierung durch die
Prufung auf Mono-Nitronaphtalin zu erkennen.
Hierfur wird eine Probe des Dinitronaphtalin abgesaugt, gewaschen, mit
Filtrierpapier so gut wie möglich getrocknet und mit Schwefelsäure 660 verrieben. Die Schwefelsäure soll sich hierbei zur
gelblich färben. Eine Rotbraunfärbung zeigt Gegenwart von Mononitronaphtalin
an. Der Kessel inhalt muss, indiser
Falle noch langer auf 800 gehalten werden oder so ..(胶卷不清!), wenn bei der Nitrometerprobe weniger als
8 cm3 NO erhalten werden, noch Salpetersäure nochgegeben werden. (这里告诉你如何知道有一硝化物!)
Nr. 4569-0. Dinitronaphtalin roh. (Gemisch 1,8 und
1,5-Dinitronaphtalin mit Harz. 1937年3月3日生产工艺。
Apparatur: (Lu 29). 设备: 同上不再分项。
(200) 1 Kessel, Gusseisen mit Universalbad, Blattrührer
n=25, Motor 3.8 Kw 3.4 m3。 (201 u. 202) 2
Nitrierkessel, Schmiedeeisen mit Universalbad, Blattrührer, n=75 bezw 71, Motor
3.8 Kw 3.4 m3。 (53) 1 Messgefäss
für dünne Salpetersäure, V2A 1.2 m3。
(207) 1 Rührkessel verbleit und auf Kerasolith
ausgemauert, Verdünner, Blattrührer n=30, Motor 3.7 Kw 14.9 m3。 (204) 1 Nutsche, Flusseisen, Kerasolithiert 8
m2 6 m3。 (203 A) 1 Druckfass auf Kerasolithiert 4 m3。
Ausgangsmaterialien: 原料: Naphtalin rein. Schwefelsäure
98%. Salpetersäure 53%.
Ammonnitrat tech.
Arbeitsweise: 操作步骤:
Im Kessel (200) werden 1985 kg Schwefelsäure 98% (=66
cm) vorgelegt, 177 kg Ammonnitrat 100% entspr. Ca. 182 kg techn. eingetragen, wobei die Temperatur um etwa 300
steigt (Abstich 71 cm) und aus Messgefäss (53) 960 kg Salpetersäure 53% unter
Keuhlung bei 300 einlaufen gelassen (Dauer ca. 2-4 Stunden, Abstich 107
cm). Der Inhalt von Kessel (200) wird
dann nach Nitrierkessel (201 bezw. 202) gedrückt (Abstich 107 cm). In die Kessel werden durch Transportschnecke
mit verschiedenen Riemenscheiben 500 kg Naphtalin rein in Schuppen eingetragen
und zwar 155 kg innerhalb 21/2 Stunden bei 34-360 mit der mittelgrossen
Scheibe, 310 kg innerhalb 7 Stunden bei nach der Hälfte von 36 auf 400
steigender Temperatur mit der grossen Scheibe,
Der Rest von 125 kg wird noch langsamer in 51/2 Stunden auf 800 geheizt
und 1 Stunde gehalten (Probe). Die Kessel werden dann einzeln nach (207)
abgelassen, wo 70 cm = 3.3 m3 Wasser vorgelegt sind. Die Temperatur steigt dabei auf 40-500. Man kühlt auf 300 und lässt auf Nutsche 204
ab. Die Mutterlauge misst ca. 260Be‘. Sie läuft über Druckfass (203 A) frei
ab. Auf der Nutsche wird des Produkt von
jeweils 2 Nitrierkessel gemeinsam mit 6 m3 kaltem und dann noch mit 12-14 m3
heissem Wasser gewaschen, die jeweils frei ablaufen. Am Ende misst das Waschwasser etwa 0.20Be‘. 100 ccm davonverbrauchen ca. 3 ccm n
Natrolauge. Mit Druckfass 203 A wird
dann trocken gesaugt und im Schildeschrank auf Al-Blechen bei 70-800
getrocknet.
Ausbeute: 收率: Pro Partie =
2 Nitrierkessel. 2000 kg
Dinitronaphtalin roh tel quel. Reingehalt
ca. 80%.
Theoretische Ausbeute:
213% einer 80%igen Ware bezogen auf Naphtalin.
Betriebsausbeute: 170% =80% d. Theorie.
Ergänzung zur
Fabrikationsvorschrift von 3.3. 1937.
1939年1月20日,为1939年3月3日生产工艺的补充。
Apparatur: 设备: 201和202 设备有改动,如下。
201 u. 202. Die
Blattrührer sind durch Fingerrührer mit Strombrecher ersetzt
n=26, Motor 3.8 Kw.
Ausgangsmaterial:
原料: Ammonnitrat
wird nicht mehr verwendet. 原料中已不再使用硝酸铵。
Arbeitsweise: 操作步骤: 改动如下。
In Kessel 201 und 202 werden je 1850 kg Schwefelsäure
98% vorgelegt. Dann laufen bis 300 1220
kg Salpetersäure 53% ein. Hierauf werden in jeden Kessel 590 kg Naphtalin rein
krist. in folgender Weise eingetragen.
118 kg in 4-4.5 Std. bei 34-360。 118 kg in
4-4.5 Std. bei 36-370。
118 kg in 5 Std. bei 36-370。 118 kg in 5-5.5 Std. bei 36-370。
118 kg in 7-8 Std. bei am Ende steigend bis zu 440. Das Dinitronaphtalin schliesst bei genauer
Einhaltung dieser Vorschrift weniger Mononitronaphtalin und Säure ein. (这里基本上与BIOS
1152 接近)。
PB 70058, 9107-9114.
Dinitonaphthalene. 1945年9月21日德文生产工艺。未査阅也未抄录。
本胶卷是根据美国人的PB报告资料抄录的题目。
国内研究动态:
宁潜济 陈文友 (天津市程村化工厂)。 α-二硝基萘的合成及应用。
[J] 染料工业,1981, 6, 35-37.摘录如下。
1α-二硝基萘的旧工艺过程是: 以部分硝化混酸为底酸,加入精萘和98%硫酸,97% 硝酸在50-55℃反应3小时。静置,分离废酸,热水洗物料至中性,得一硝基萘。
再将一硝基萘加四倍硫酸,降温至0℃, 加入硝化混酸,升温,于70℃硝化。静置,分酸,水洗,得1,5-和1,8-混合二硝基萘。
新工艺的改变主要有: 1. 把二次硝化改为一次二硝化。成功的关键在于严格控制物料比,尤其是混酸的配比,使硝化反应在稳定的D.V.S.值下进行。 2. 采用低毒的溶剂分离1,5-和1,8-二种异构体,溶剂为酒精,醋酸等几种溶剂按一定比例组成的混合物,利用不同温度下二种异构体的不同溶解度来分离。 3. 提高硝化温度。实践表明,这是完成一次二硝化反应的另一关键,而且在改变温度和改变硝化时间后可以根据需要改变产品中1,5-和1,8-二种异构体的含量比。 4. 不用精萘,在新工艺的条件下完全克服了粗萘中蒽油及其他杂质对反应的干扰。 参考文献: [1] BIOS, No.
986.
王贤丰 徐炳辉 (沈阳工业大学) 刘晓梅 (染料国家工程研究中心)。 1,5-二硝基萘及1,8-二硝基萘的提纯。
[J] 染料工业, 1998, 6, 35-37. 摘录如下。 (部分抄录不再分项!)。
1. 单一溶剂分离实验方法: 1.
1 二氯乙烷法: 将二硝基萘混合物分散于二氯乙烷中(3.5 ml 二氯乙烷/ 1 g 二硝基物),搅拌下升温到85℃并维持半小时,然后降温到50-52℃并于此温度下搅拌半小时,接着趁热过滤出富含1,5-二硝基萘的滤饼,该滤饼水洗后干燥。所得滤液浓缩至原体积的一半后冷却到室温,静置半小时,过滤出富含1,8-二硝基萘的滤饼,干燥后以气相色谱测其含量。 1. 2 丙酮法: 将二硝基物分散于丙酮中(8.5 ml / 1 g 二硝基物),搅拌下升温至回流并维持2小时。然后降温至48℃,趁热过滤出富含1,5-二硝基萘的滤饼,水洗后干燥,分析其含量。趁热过滤的滤液浓缩到原体积的三分之一,于室温下过滤出富含1,8-二硝基萘滤饼,水洗后干燥,测其含量。 1. 3 其它溶剂分离法: 以甲苯,乙酸,二甲基甲酰胺未溶剂分别1:3.1,
1:7.5, 1:1.1 (二硝基物重量 g : 溶剂体积 ml)比例,于75℃, 90℃,35℃下分离,分离出的各组分干燥后测其含量。
2. 用无机物 – 有机溶剂分离于精制的实验方法: 略。
参考文献: 4篇。(未见上述生产工艺历史文献。)。
随想:
熊啓渭 等 译《中间体及染料合成原理》《Основысинтезапромежуточныхпродуктвикрасителей》1955年出版。 P. 175. 其中萘的二硝化和混合物的二氯乙烷为溶剂的分离法。引用文献如下。
н. н. Ворожцов мл., Хим. Пром., 1947, No. 6, 21. (这是俄文化学工业)。
н. н. Hodgson, J. S.
Whitehurst, Soc., 1945, 202. 回顾俄文图书,基本上未见引用BIOS,FIAT。PB报告更不要说了!
今天再次抄录一些德文原件,希望读者理解,早在1945年以前,他们已用丙酮法和二氯乙烷法进行二硝基萘的分离,而且有具体生产工艺,可惜这些资料无人整理归纳,而我们还在研究。当然这是历史文献,是否有用请读者看吧!
陈忠源 2017年11月23日













