C.I. 冰染重氮组分1 (C.I. 37135) 生产工艺 CAS号 [96-96-8]
CAS名: Benzenamine, 4-methoxy-2-nitro-, 参考文献: Beil. 13, 521.
发明者: Laska, Zitscher 1923年。
生产工艺文献: 原版Colour
Index - FIAT 764 – Echtbordo GP Base. Echtbordosalz GP kz.
BIOS 986, 285-290. (=胶卷PB 77764) No.156 3-Nitro-p-anisidine crude moist. I.G. Offenbech. 英国人译自德文。抄录如下。
反应式: 本人有改写,有加注。 译者未注明译自哪个PB报告和它的生产工艺年份。产品编号:3550 – 0. 答案,见后。
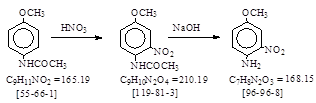
1. Nitration. Charge. [55-66-1] + HNO3 à
[119-81-3] + H2O
(a) Theoretical. 300 kg + 114.5 kg à 318.8 + 32.8 kg
(b) Practical. 300 kg + 137.6
kg à 364 kg (1.82 mol.) (120.2% of theory.)
2. Hydrolysis. Charge. [119-81-3]
+ NaOH à
[96-96-8] + CH3COONa
(a) Theoretical. 364 kg + 69.3 kg
à 291.2 kg +
82 kg
(b) Practical. 364 kg + 100 kg à 284 kg (144.3% of theory)
Yield: 284
kg. 3-nitro-p-anisidine crude moist as 100% = 93% of theory.(Dried material has an average purity of
94.6%).
Process: Raw
Materials: p-acetanisidide
100% 300 kg. HNO3 100% as nitric acid 400Be’ 137.6 kg.
Rock salt 150 kg. Chlorobenzene 750 kg. NaOH, 100% as 50% liquor 100 kg.
(1) Nitration: 原件按德文以投料量分项,抄录文不再分项。
750 kg.
chlorobenzene, 150 kg. rock salt are charged into the nitrator followed by 34.4 kg. HNO3 as nitric acid 400Be’ = 41 litres (56 kg. actual weight). Then during
approx. 3 hours, 300 kg. p-acetanisidide are charged through the tundish and simultaneously 103.2 kg HNO3 as nitric acid 400Be’ = 132 litres (168 kg actual weight.). The
reaction temperature is controlled at 20-300C, during the addition of the acetanisidide by external
cooling (with water or ice according to season). Agitation is continued for 1 hour at 300C. after
completion of the charge. 31 kg. soda
ash is then added, when there should be a weakly alkaline reaction. The
contents of the nitrator are sucked into the still and the chlorobenzene is distilled off with live steam through the
condenser. The condensate is separated in the overflow separator and the
chlorobenzene passes to the storage tank (item No. 4.).
Time of distillation approx. 5 hours.
(2) Hydrolysis:
After the chlorobenzene is blown off, the mixture is
cooled to 700C. and 100 kg. NaOH as 50% solution is blown
in. The volume is then made up to 1950
l. with water. The temperature falls to 450 to 500C. The mixture is then carefully
heated to 750C. and is
maintained at 750 to 770C.
for 2 hours. The contents of the pan must be maintained alkaline. The
hydrolysis is finished when the melting point of a sample is 1230 to 1240C. Cool
to 300C., blow the contents of the pan to the iron vacuum filter
and wash the residue free from alkali. Product which has been sucked dry is
packed into cakes. Crude nitro-p-anisidine No. 3550 is used internally as the
moist product and worked up to the colour base. For preparation of
nitro-p-anisidine No. 3550 crude, dry, the material is dried in a vacuum drying
stove at 950C. and ground
in a Toutonia mill (sieve with 2 mm. slits.).
For sale as Fast
Bordeaux GP Base, it must be recrystallised (c.f. Process for
nitro-p-anisidine No. 3550 pure, Fast
Bordeaux GP Base).
Plant: (1) Nitrator. (2) Distillation and hydrolysis vessel. (3) Iron filter. (4) Auxiliary equipment. 略。
No. 157.
3-Nitro-p-anisidine Pure (Fast Bordeaux GP Base) I.G. Offenbach.
Spec. No. 3550 – 1. 1943年6月23日。抄录如下。
Principal: Solution of nitro-p-anisidine crude, moist, Spec. No.
3550 – 0. 这里说了年份,但仍未说明译自哪个PB报告。
Yield: 93% crude charged. (Refer to process
for nitro-p-anisidine crude, moist, No. 3550 – o.
Process: Raw Materials: 194 kg.
nitro-p-anisidine, crude, moist. Spec. No. 3550 – 0.
20 kg. Carboraffin (or
30 kg. decolourising carbon TO) 2
kg. Soda ash.
Prcedure:
Into the dissolving vessel (1) are charged 12,000 litres water or mother liquor
from a previous batch, 20 kg.
carboraffin, dry, or as 331/3 wet carbon (or 30 kg. decolourising carbon TO), 2 kg. soda ash. About 194
kg. nitro-p-anisidine, crude, moist, calculated on dry basis, corresponding
to about 2/3 of a nitration and saponification batch (see
process for the crude, No. 3550 – 0), are shoveled in.
The air is displaced from the dissolving vessel by
steam, the vessel is closed, and steam is blown on the surface, (of the liquid)
until a pressure of 2 ats. is
reached. After 20 mins. At 2 ats. pressure,
stirring is stared, and the batch is blown with compressed air through the
filter press into the cooling vessel. After cooling to 400C. it is blown to the vacuum filter. The filtrate is
used for dissolving the next batch. The excess of mother liquor resulting
condensation of steam is discarded. The wet residue (i.e. carbon) from two
batches is extracted in the same way with mother liquor in the dissolving
vessel. The wet cake from the filter is dried at 950C. in the vacuum stove, and then ground in the Toutonia mill.
The Fast
Bordeaux GP base has a purity of 99.5
– 99.9% and a m.p. of about 125 –
1260C.
Plant: (1) – (4). 略。
细田豊。《理论制造染料化学》1957年。P. 655. 摘译自PB
77764. (未注明页号和BIOS号)抄录如下。
3-ニトロ-4-アニシシ’ン。本文与德文的英译文,相差14年。
クロルヘンセン750 kg, NaCl 150 kg,
400Be’硝酸34.4 kgの中にp-アセトアニシシ’ン300 kg と400Be’硝酸103.2 kgを同时に20-300て”3 hかかつて加え,300て”1 h搅拌する。
Na2CO3 31 kg
て弱アルカリ性とし,水蒸气蒸留によつてクロルヘ”ンセ”ンを追出し,700て”NaOH 100 kgを50%液て”加え水て”1950 l.となし, 75-770に2
h加热してアセチル基を加水分解し,300て”滤洗する。284 可供100%,收率93% (纯度94.6%)。
精制 (Fast Bordeaux GP
Base)
水または前回母液12 m3,活性炭20-30 kg Na2CO3 2 kgの中に粗制194 kgを湿つたまま加え,水蒸气て”空气を追出し,密闭して水蒸气を表面に吹き付けて2 气压となり20 m後搅拌し,滤過して滤液を400に冷し滤洗する。收率93%,纯度99.5-99.9%。
mp 125-1260.
张澍声。 《精细化工中间体工业生产技术》 1996年。 P. 15-16. 摘译自BIOS 986,288.。这里已相差50年。请见原书。
PB 25626, 1705-1706.
3-Nitro-4-anisidin “Echtbordo GPP
base” 1939年5月。德文生产工艺。1美元。未抄录。
PB 70422, 1873-1875.
P-Acetanisidine [57-66-1] 德文生产工艺。1943年5月25日。1.5美元。未抄录。
PB 70422, 1876-1881.
Nitro-p-anisidine, crude wet. [96-96-8] 德文生产工艺。1943年6月1日。1.5美元。未抄录。
PB 70422, 1882-1886.
Nitro-p-anisdine, pure. [96-96-8] 德文生产工艺。1943年6月23日。1.5美元。未抄录。
经部分摘录核实,BIOS 986, 285-288是德文生产工艺原件的摘译文!因原件未抄录,不能评述。当然,原件更可靠!
上海中国染料三厂 紫酱GP色基之操作。 [J] 有机化学工业技术报导。 1959,9,63-64. 这里相差14年。生产工艺已有改动。
1. 乙酰对氨基苯甲醚的硝化.(无参考文献)
375公斤氯化苯加入硝化锅中,搅拌,将24公斤硝酸(62%)慢慢加入,加热到250C以上,再将150公斤乙酰对氨基苯甲醚(分四批剩余2公斤)及88公斤硝酸62%(亦分四批)同时分别按比例加入,先加乙酰对氨基苯甲醚,加料时发生热量,必须维持硝化温度在25-300C 之间,并以适当冷却控制,硝化的正常温度为23-270C,全部加料时间约4-6小时。硝酸先加完,然后将剩余的2公斤乙酰对氨基苯甲醚加完,加料先后注意控制冷却盐水循环,保持温度在28-300C之间1小时,使之稳定,将夹层盐水放出,再升温至300C, 保持半小时,取样测定,隔点应在1130C以上,然后再慢慢冷却到100C, 起初每5分钟冷却10C, 200C以下加快冷却速度,放出滤液,滤饼再用水清洗至中性,再到烘箱中在700C烘干。 成品为老黄色粉末。
2. 间硝基对乙酰氨基苯甲醚的水解.
水解锅中先放水1,000升,搅拌,将已干燥的间硝基对乙酰氨基苯甲醚加入,在室温下搅拌1小时,使成均匀状态后,将169公斤29.5%液碱加入,开始升温,起初升至500C, 此阶段可以稍快一些,500C以上应徐徐升高,约2-3分钟升高10C,在750C时应先停止加热,不使温度超过770C, 如超过时,应即通入冷水冷却,溶液变成红棕色,维持温度在75-770C之间2小时,取样测定,熔点须在1210C以上,通入冷水慢慢冷却至150C(或加水稀释冷却到150C)再过滤,并用清水洗涤至不呈碱性为止,取出滤饼烘干即可。
上海染料生产工艺汇编,210-211 (1976) 紫酱色基GP 生产工艺。抄录如下。
1. 硝化: 硝化锅内放入400升氯苯,200公斤对乙酰氨基苯甲醚及0.5公斤亚硫酸氢钠,调节温度至280C, 然后将61%硝酸162.3公斤于4小时加入,,开始2小时加入3/5,
后2小时加入2/5,
控制反应温度在25-300C, 加料过程中每小时再加入0.5公斤亚硫酸氢钠。加毕,于25-300C保温1.5小时。加水,静置后分去上层水。硝化物供水解。干品熔点≥1140C.
2. 水解: 水解锅内放水900升,吸入上述硝化物及10公斤亚硫酸钠,校正pH = 7-7.5.蒸馏,脱氯苯。冷至400C,加入30%液碱200公斤。然后与1小时内小心升温至76-770C,保温2小时。冷却至300C. 压滤,滤饼用300C热水洗至中性,干燥。干品熔点≥1210C. 总收率:80%。
素砚奚。枣红色基GP合成工艺的改进。[J] 染料工业, 2002,4. 11-12. 本文重点是用二氯乙烷酰化。摘录如下。
合成操作:
将1,2-二氯乙烷50毫升。醋酐0.13毫升加入装有搅拌器,滴液漏斗,冷凝器和温度计的四口烧饼中,在搅拌下慢慢加入0.1mol对氨基苯甲醚(12.3g),在850C下保持2小时,降温至100C – 150C下保持3小时。将硝化液倒入冷水中,洗去游离酸并回收溶剂,再经碱性水解得暗红色棱状晶体粉末枣红色基GP. 产品熔程128-1300C.
抄注: 参考文献:无上述文献。不知为什么?
加注:
当前,提出中国制造应为中国智造,即互联网 + 信息化 + 工业化。从上述抄录文献可以看出,我们的信息化还有一定差距,例如冰染重氮组分1,有色基和色盐(显色盐),原版Colour
Index 只有名称Echtbordo
GP Base 色基和Echtbordosalz
GP.色盐。所以国内的染料品种手册(世界染料品种 – 2000年和2005年),也只列出色基和色盐名称。
其结构式如下:

色基 重氮体 色盐
色盐的生产工艺: 含重氮化和成盐。
PB 25628, 3461-3463 Echtbordosalz GP 1937年7月。 2美元。未抄录。
PB 70422,2108-2109. Echtbordosalz GP 1937年7月21. 1.5美元。生产工艺编写者:Prosiegel. 未抄录。
其次,文献的摘录问题,国内没有系统的收录,所以有的会出现重复研究或不知道别人早已研究以及早已有生产工艺的问题,典型的例子是PB报告,我们比日本落后多了,请看细田豊的理论制造染料化学。
为什么美国化学文摘,至今大家还在用?而且要化大钱,我们为什么没有?至少应该不能忘了自己的文献收录!
陈忠源 2016年10月24日 于 无锡 明辉国际。













